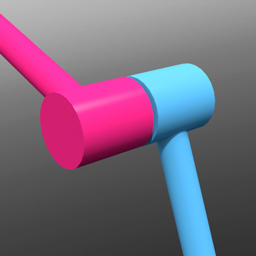
The Hinge Constraint limits the rotation movement of an object to swivel as if fixed by a hinge joint like that of a door. However, as a door hinge is limited by the collision of the opposing hinge plate, the hinge constraint offers unlimited rotation, much like a wheel axle. Users can add a rotation range limit to the joint to produce the more limited motion of the door hinge. The Hinge constraint is represented in the viewport as a circle around the point of rotation.
To apply a constraint automatically, users can select two items prior to invoking any of the Constraint types. The first item selected represents the master or parent item and will be populated as 'Body A' within the constraint, the second item selected will be the item that is constrained, also considered the auxiliary or child item and will be populated as 'Body B'. With the items selected, LMB+click on the 'Hinge' constraint button, adding the constraint item to the 'Items List'. The default center location (position) of the Hinge Constraint will be exactly half-way between the Body A and Body B objects with a line drawing to the centers of the constrained items. Depending on your intentions, this might not be the optimal position for the Constraint. The motion of the child item (Body B) will originate from the position of the Constraint item itself, so it may need to be positioned appropriately.
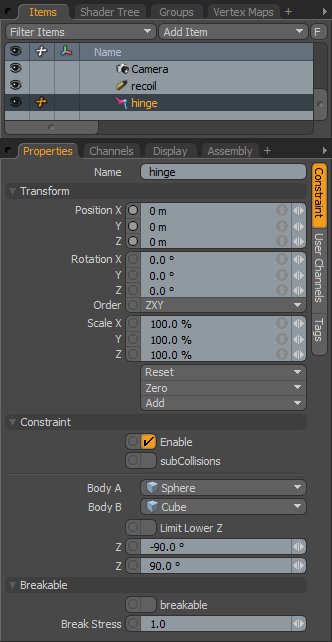 Name: This data field displays the current Constraint item name. Users may easily change it by LMB-clicking within the field and typing the new name.
Name: This data field displays the current Constraint item name. Users may easily change it by LMB-clicking within the field and typing the new name.
Transform--
Position X/Y/Z: The Position XYZ values represents the initial center for constraint item in 3D world space, it also represents the center of mass relative to the item it is constraining. Based on its initial position, once a dynamics simulation is invoked, the constraining item will rotate and move based on this initial (resting) position.
Rotation X/Y/Z: The Rotation XYZ value represents the initial (resting) rotation of the constraining item.
Order: The 'Order' option allows the user to set the order that rotations are applied to the item, each producing a different result. Changing the order that rotations are applied can sometimes help to reduce or eliminate gimbal lock.
Scale X/Y/Z: The Scale XYZ values have no direct affect over Constraints.
Reset: Resets the selected transform values to (0,0,0) returning the item back to its default state.
Zero: Resets the chosen transform property values to '0', leaving the 'Center' position intact.
Add: The 'Add' function will add the selected set of transforms to the channel list. Useful when keyframe animating complex motions, providing a layered approach to the applied transforms. There are no benefits to applying additional transforms to dynamic objects.
Constraint--
Enable: The 'Enable' option toggles the Constraint item on or off. When enabled the constraint item will be considered during a dynamics simulation, when disabled, the constraint item will be ignored. However, disabled constraints are persistent across modo sessions being saved with the scene, and retain their present settings.
SubCollisions: The 'SubCollisions' option, when enabled, allows constrained objects (especially those within a chain, not a literal chain but subsequent groupings) to collide with one another. When disabled (the default state), fewer calculation are required, however, constrained items may inter-penetrate each other. If this occurs users will want to enable SubCollisions.
Body A: The 'Body A' setting represents the item that is constrained to, this could also be considered the parent or master item.
Body B: The 'Body B' setting represent the item that is constrained, this could be considered the child or auxiliary item.
Limit Lower Z: The hinge Constraint is not initially limited in its rotation which by default is around the 'Z' axis. This way opposing objects can spin freely against each other, like a wheel or a propeller. By enabling the 'Limit Lower Z' option, users can limit the range or rotation that can be applied to the hinge constraint, mimicking the traditional range of motion of a door hinge that is allowed to only swing so far.
Z Minimum/Maximum: The first Minimum value sets the lower extreme of the of the rotation clamping, while the second Maximum value limits the upper extreme value.
Breakable--
Breakable: The 'Breakable' option allows constraints to literally be broken apart when a certain stress threshold is reached, defined by the 'Break Stress' value. When the threshold is reached, the constraint will no longer have any affect on the constrained item, leaving it to be affected by any other forces present in the simulation.
Break Stress: The 'Break Stress' value determines the threshold when the constraint will no longer affect the constrained item. The 'Breakable' option must be enabled for this value to have any affect on the constraint.


