Accessible from the menu bar under "System > Preferences...", the modo preferences define the default behavior for a variety of options and functions in modo, further customizing the application to suit users particular tastes and needs. The Preferences are categorized into four main functions- Input deals with ways users interact with the application, 'Display' controls the various way viewports display geometry and information. The 'Data' section controls default behaviors for data created in modo and finally 'File I/O' controls how scenes are imported and exported when dealing with external applications.
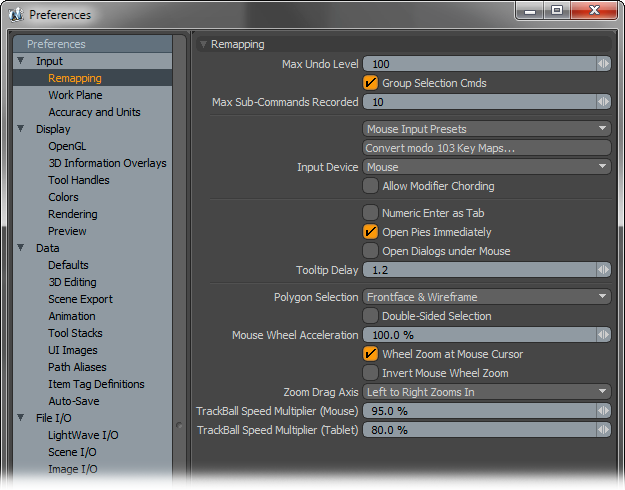
Max Undo Levels: The undo history is viewable within the 'Command History' viewport. The 'Max Undo Levels' controls the maximum number of steps backwards users can go in the history. The default value of '100' is generally very good at allowing users leeway to step backwards through the history. Increasing the value will allow users to go further back in time, so to speak, but will also increase memory usage. For memory intensive scenes, it may be beneficial to reduce this value to reduce memory overhead.
Group Selection Cmds: When this option is enabled, modo will group multiple consecutive selection actions into a single undoable action. The grouping size is determined by the 'Max Sub-Commands Recorded' Value.
Max Sub-Commands Recorded: This option determines the maximum number of selection commands that can be grouped into a single undoable action. 'Group Selection Commands'
Mouse Input Presets: Users coming to modo who are familiar with another 3D application might find themselves unable to switch into modo mode. The 'Mouse Input Presets' are meant to adjust the mouse navigation controls to mimic those of the chosen application reducing users navigational stumbling, making it easier for switching back and forth between the other program. A variety of options are available representing a number of popular 3D programs.
Convert modo 103 Key Maps: This legacy option converts modo 103 keymaps to the current version. User would need to load v103 keymap configs using the 'Config Import' function found in the file menu prior to running this option.
Input Device: This option determines how modo interprets input commands, users can choose either a 'Mouse' or 'Tablet' as the main form of input. Tablets typically use an absolute positioning based on a stylus' position on the tablet surface, whereas a Mouse uses a relative position based only on the initial position of the cursor. Users using a Tablet with relative positioning should set this option to 'Mouse'.
Allow Modifier Chording: When enabled, modifier keys can trigger 'Chording', when disabled, only mouse buttons can trigger chording. Chording is the use of multiple mouse buttons simultaneously. It should be noted that chording has been widely recognized as a key contributor to carpal tunnel syndrome and other repeated stress injuries. Luxology recommends that users avoid chording to prevent unnecessary muscle strain.
Numeric Enter as Tab: When enabled, pressing the 'Enter' key on the numeric keypad will function the same way as pressing the Tab key does, by advancing the cursor to the next logical data field.
Open Pies Immediately: This option determines weather there is a slight delay to the opening of Pie Menus when disabled, or if the menus open immediately when enabled. For users not accustomed to Pie Menus, the delay may be helpful in eliminating menus from popping open unexpectedly on errant key presses.
Open Dialogues Under Mouse: This option forces new dialog boxes to always open at the current mouse position (such as the 'Save As' and 'Open' file dialogues). When disabled, dialog boxes will open in the same position as the last open dialog box.
Tooltip Delay: Defined in seconds, this option determines the length of time before the tooltip info display opens when hovering the mouse pointer over a button or function of modo. The default value is 1.2 seconds.
Polygon Selection: This option determines the behavior of lasso or paint selection modes when selecting components in the OpenGL viewports.
Frontface & Wireframe- Default behavior is only forward facing polygons are selected, except when in Wireframe mode where both the front and back facing polygons are selected.
Frontface & Backface-
Default behavior is front and back facers are always selected regardless of viewport style.
Frontface only- Default behavior is to select only front facing geometry regardless of viewport style.
Always Raycast- Probably means something important
Double Sided Selection: When this option is enabled, any polygons tagged with a material that is defined as 'Double Sided', users can then paint select these polygons from their back side. When disabled, users are unable to paint select polygons from the back.
Mouse Wheel Acceleration: This percentage value determines the speed at which modo zooms in or out when using a mouse's scroll wheel. Higher values will zoom faster, while lower values will zoom more slowly.
Wheel Zoom at Mouse Cursor: When this option is enabled, zooming in any OpenGL viewport with the mouse scroll wheel will center the zoom based on the mouse's position over the viewport, when disabled, the mouse's position is disregarded and the viewport will zoom based on its center.
Invert Mouse Wheel Zoom: This option inverts the zooming behavior of the mouse wheel. Pushing forward on the wheel will push out instead of in.
Zoom Drag Axis: This option determines the directional behavior when hauling in a 3D viewport when zooming. The options are 'Left to Right', 'Right to Left', 'Bottom to Top' and 'Top to Bottom'.
Trackball Speed Multiplier: This option determines the rotation speed for using Trackball rotation when navigate in an OpenGL viewport. There are separate settings for both 'Mouse' and 'Tablets'.
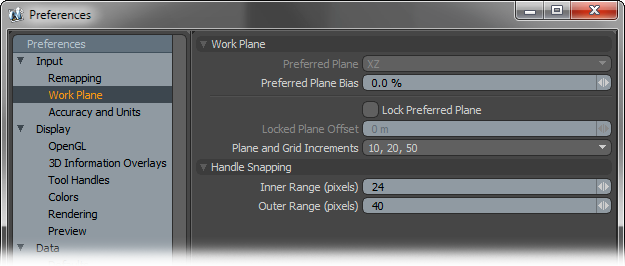
Workplane--
Users can favor certain planes when using the Work Plane, especially in instances where users don't want to lock the plane, but it would be helpful to have it face a certain direction, such as modeling a rough city, users could rotate the views but keep the Work Plane mostly facing upwards (like it was the ground) when creating new geometry.
Preferred Plane: When the 'Preferred Plane Bias option is set above 0%, uses can choose a preferred Work Plane. Based on the bias amount, modo will attempt to keep the workplane positioned at the preferred plane determined by its two major axes.
Preferred Plane Bias: When working with the Work Plane, modo tries to keep the plane perpendicular to the viewport window when navigating and rotating the view. Increasing the Plane Bias option will increase modo's favor of the Preferred Plane. Setting a very high value means modo would almost always favor the preferred plane.
Lock Preferred Plane: Users may also prefer to lock the Work Plane to a specific plane facing direction by enabling this option. Once fixed, rotating the viewport will have no effect on the position or angle of the workplane.
Locked Plane Offset: When the Work Plane is locked, users can additionally set an offset (from the origin), providing accurate control over the position and placement of the workplane when used as a construction plane.
Plane and Grid Increments: As users zoom in and out of a scene, the Work Plane grid adjusts the density of the grid divisions adding or removing subdivisions based on the Plane Increments. Users can modify this behavior using this option.
Handle Snapping--
These are the default values, in pixels, for the distance from a snapping target where the cursor first gets snapped.
Inner Range: Determines the actual snapping range.
Outer Range: Determines the range to highlighting elements for snapping to.
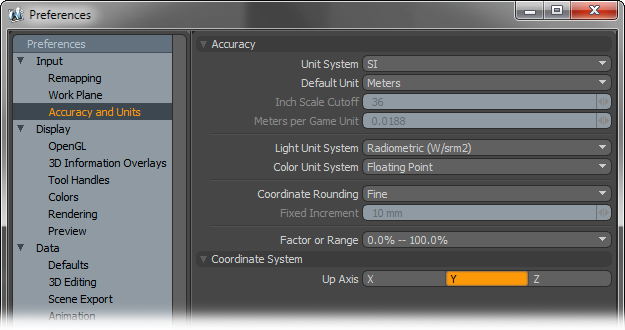
Accuracy--
Unit System: Users can choose their preferred measurement units system based on several options. Once set, this is the measurement input method modo will use for all numerical input values-
SI- The International System of Measurement (abbreviated 'SI') is the modern form of Metric, complies to universal base units.
Metric- A universal system of measurement based on powers of '10' -millimeter, centimeter, meter, kilometer.
English- A historical measurement system based on Imperial Units -mils, inch, foot, yard and mile
Game Units- An arbitrary unit of measurement (defined by the 'Meters per Game Unit' setting).
Unitless- An arbitrary decimalized unit of measurement based on cubic meters, essentially 1 unit = 1m.
Default Unit: This option is dependant on the 'Unit System' and determines the default unit used when no unit is specified.
Inch Scale Cutoff: When the 'English' Unit System is selected, the 'Inch Scale Cutoff' determines the cutoff where modo will display strictly inches as feet and inches. For example, when set to the default 36, 27 inches will display as 27", but 42 inches will display as 3' 6".
Meters per Game Unit: When utilizing the arbitrary 'Game Units' systems, users can use this value to determine the scale of a single unit. This allows users to work with even whole numbers. So if a 1m equivalent is really 1.375 real world meters in modo, users an simply enter 1.375 here and then specify units normally in the numerical input fields.
Light Unit System: This option determines the default Light Unit modo uses when specifying a lights brightness-
Radiometric- Measurement of the electromagnetic spectrum (which included visible light); defined by power of radiation.
Photometric-
Measurement of brightness of light as perceived by human eye; defined by luminous intensity.
Color Unit System: Determines the color unit system used for specifying colors in modo-
Floating Point- Determines colors based on decimals, uses 0-1 range (and beyond for HDR colors).
Percentage- Determines colors based on percentages, uses 0%-100% range.
Integer- Determines colors based on 8bit value scale, uses 0-255 range (2 to 8th power = 256 values)
Hexadecimal- A computer numerical system similar to binary represented by 16 characters. 2bit Hex produces 256 values, similar to Integer color units. Widely used in specifying color on the web, uses 00.00.00-ff.ff.ff range.
Coordinate Rounding: This option controls how mouse input is converted, via the Work Plane, into 3D coordinates.
None-- This means that no coordinate rounding is done. Every mouse move gives unclamped coordinates (typically with lots of decimals). This option is basically the raw 2D -> 3D transform. Useful for working freehand.
Normal-- This option attempts to give clean, round coordinates based on the users view transform; so as the mouse moves, users can see values that are nice in your current unit system display in the information tab. The step size will get smaller or larger as the user zooms in or out. Users may need to move the mouse cursor 2-3 pixels to see values update.
Fine-- This option is similar to 'Normal' but optimizes for closer to one step of coordinate rounding from one pixel of mouse movement. Gives the user finer grained input, but can be difficult to hit exact values.
Fixed-- This option uses the 'Fixed Increment' preference to put a lower limit on both coordinate rounding and the grid. If the user sets the fixed increment to 10mm that means the grid will never get finer than 10mm, and all input will be rounded to the nearest 10mm even at high zoom. When zoomed out, however, the grid will show larger values but the step size will always be a multiple of the fixed increment.
Forced Fixed-- This option is similar to 'Fixed', but forces the size of the grid and the input step to match the increment exactly no matter the zoom level.
Fixed Increment: When the Coordinate Rounding is set to either 'Fixed' options, this value determines the Fixed coordinate rounding grid.
Factor or Range: This option determines surfacing and material value units, users can specify values as a percentage 0%-100% or as a float value 0.0-1.0
Coordinate System--
Up Axis: This option determines the major axis that is considered the default up direction for modo. 3D programs typically use 'Y' as up, where CAD applications typically use 'Z' as the up direction. When importing geometry, if it is always 90° off, changing the up axis to match the originating application may resolve the issue. This can also be set on a per scene basis in the 'Scene Item'.