
The 'Hair Material' is designed to replace the default BRDF shading calculations of the standard Material item when applied to fur. Fur, or hair as the case may be, is anisotropic, meaning its shading is directionally dependent and requires a different type of shading model to look correct. On a microscopic level, the surface of hair is quite complex and this affects how light reflects off of it and how it scatters through it, producing a unique look that is difficult to simulate without a dedicated hair shader.
MODO has implemented a hair shading system using a special model for quickly approximating multiple scattering layers, which is way too expensive to compute otherwise with brute force. The model is called Dual Scattering Approximation, and is based off this technical paper. The basic idea is that multiple scattering is essentially broken into two parts: global scattering (lighting of the overall volume) and local scattering (the shading on individual fibers that are visible).
The 'Hair Material' item is added to the Shader Tree using the 'Add Layer' function -"Add Layer > Custom Materials > Hair Material". For more information on adding and manipulating Shader Tree layers, please reference that page of the documentation. For proper results, the placement of the layer is important, as the Hair Shader itself must reside in the same Group Mask as the 'Fur Material' item it is shading. Once a 'Hair Material' is added, its settings will supersede those of any Material item rendering it unnecessary. Once positioned, selecting the 'Hair Shader ' item will reveal its attributes in the 'Properties' viewport where its settings may be adjusted to fine tune the look of the rendered hair.
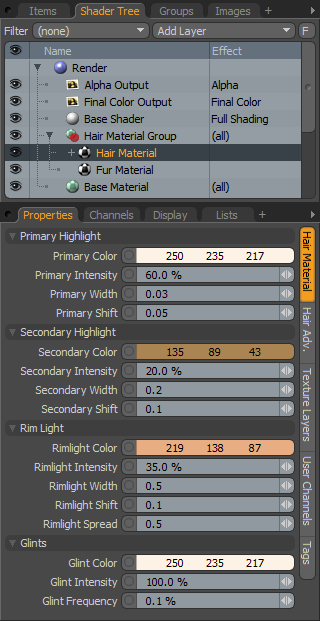 Primary Highlight--
Primary Highlight--
The 'Primary Highlight' represents the main light colored highlight that is reflected off the surface of the hair, the more apparent this highlight is, the more sheen the hair will have.
Primary Color: R,G and B values that determine the color of the 'Primary Highlight'.
Primary Intensity: The 'Intensity' option acts as a multiplier controlling the strength of the 'Primary Highlight'.
Primary Width: This option controls the size of the highlight along the hairs length.
Primary Shift: This option controls the position of the highlight along the hairs length, basically simulating the tiny shingle-like cuticles of the hair's surface that modify the angle of the reflected highlight.
Secondary Highlight--
The 'Secondary Highlight' represents light that is refracted into the hair strand, hitting the back surface and reflecting back towards the front. Realistically, the magnitude of the longitudinal shift for the 'Secondary Highlight' should be larger than for the 'Primary Highlight' because the light path will be more disrupted with additional refractions and reflections.
Secondary Color: R,G and B values that determine the color of the 'Secondary Highlight' shading.
Secondary Intensity: The 'Intensity' option acts as a multiplier controlling the strength of the 'Secondary Highlight'.
Secondary Width: This option controls the size of the highlight along the hairs length.
Secondary Shift: This option controls the position of the highlight along the hairs length, basically simulating the tiny shingle-like cuticles of the hair's surface that modify the angle of the reflected highlight.
Rim Light--
The 'Rim Light' represents light that is transmitted through the hair similar to the effects of subsurface scattering.
Rim Color: R,G and B values that determine the color of the 'Rim Light' shading.
Rim Intensity: The 'Intensity' option acts as a multiplier controlling the strength of the 'Rim Light'.
Rim Width: This option controls the size of the highlight along the hairs length.
Rim Shift: This option controls the position of the 'Rim Light along the hairs length, basically simulating the tiny shingle-like cuticles of the hair's surface that modify the angle of the reflected highlight.
Rim Spread: Controls how broad or tight the Rim Light highlight is, similar to a specular highlight in a sense.
Glints--
Glints are representative of tiny caustics refracted through the
hair, basically this is how hair looks shimmery.
Glints Color: R,G and B values that determine the color of the 'Glints' shading.
Glints Intensity: The 'Intensity' option acts as a multiplier controlling the strength of the 'Glints'.
Glints Frequency: Determines how often a glint is shaded, controlling the overall density of 'Glints'.
Hair Shader Advanced
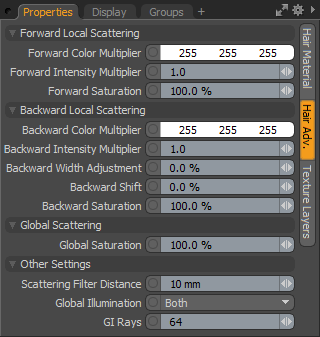 Forward Local Scattering--
Forward Local Scattering--
This controls how multiple fibers in a small area will scatter light forward, or away from the source of light. It contributes to the appearance of rim lighting, but it is wider, darker, and the color is more saturated than direct rim lighting. This is because the light is scattering multiple times, making it spread out more.
Forward Color Multiplier: This setting allows the user to adjust the color of the forward local scattering, by multiplying the color values. So when each color channel is set to 1.0 (when the color is white) the forward local scattering color is only dependent on the colors in the hair material settings overall.
Forward Intensity Multiplier: This allows the user to make the forward local scattering brighter or darker, by multiplying the value.
Forward Saturation: This allows the user to control the color intensity of the Forward Local Scattering, making it more or less colorful.
Backward Local Scattering--
The backward scattering adjustments represent areas where the hair is front lit, but the specific hair strand is in shadow.
Backward Color Multiplier: This setting allows the user to adjust the color of the forward local scattering, by multiplying the color values. So when each color channel is set to 1.0 (when the color is white) the forward local scattering color is only dependent on the colors in the hair material settings overall.
Backward Intensity Multiplier: This allows the user to make the forward local scattering brighter or darker, by multiplying the value.
Backward Width Adjustment: This option controls the size of the highlight along the hairs length, relative to the initial width, adjusting it wider or thinner.
Backward Shift: This option controls the position of the highlight along the hairs length, relative to the initial 'Shift' value, moving the color of the backward scattering along the length of the hair strand.
Backward Saturation: This allows the user to control the color intensity of the Backward Local Scattering, making it more or less colorful.
Global Scattering--
Global scattering controls the way in which light transmits, scatters, and spreads through a whole volume of hair. It is brightest and least spread out closest to the light, and gets dimmer, more spread out, and more colorful as the light transmits through more strands of hair. It will affect both forward and backward multiple scattering.
Global Saturation: This makes the global scattering less colorful. In particular, if the rim lighting setting of a hair is too bright or wide, it can cause the color of global scattering to blow out because some color channels lose very little energy as they're transmitted through the hair while other channels lose exponentially more energy. This can be used to compensate for that effect.
Other Settings--
Scattering Filter Distance: The Hair Material uses advanced calculations to approximate the multi scattering from light in dense fiber clusters. This estimation could occasionally produce sharp discontinuities which would appear as noise that no amount of samples would clear up. The 'Scattering Filter Distance' adds a random offset to the origin of the ray used to estimate the scattering. This effectively converts the sharp discontinuities into actual noise that will go away with more antialiasing samples. Note that large filtering distances can also add illumination bias, shifting the overall brightness of the hair, but when applied sensibly it works very well.
Global Illumination: When illuminating hair (or fur) using Global Illumination, users can adjust the 'Global Illumination' settings of the hair shader to control how the GI rays are used--
None- This means that the color of the hair is only affected by direct and ambient lighting. It also doesn't bounce light onto other surfaces.
Receive Indirect Lighting- Receiving indirect lighting means that light will bounce off other surfaces onto the hair, causing the hair to be lit indirectly. This is done with Monte-Carlo global illumination, by casting rays in every direction, instead of just towards a light.
Cast Indirect Lighting- This means that the hair will contribute indirect lighting onto other surfaces. In other words, indirect rays being fired from another surface will cause the hair shading to be evaluated if they hit the hair surface, instead of just appearing black.
Both- This does both Receiving and Casting of indirect lighting.
GI Rays: This controls how many rays will be used for calculating indirect lighting, either in the 'Receive' or 'Both' modes. More rays will produce smoother results at the expense of longer render times.
Texture Layers
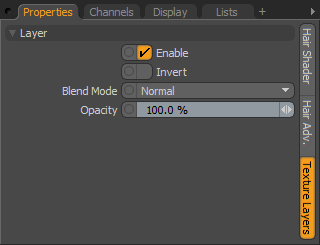 Layer--
Layer--
Enable: Toggles the effect of the layer on and off, duplicating the functionality of toggling visibility in the Shader Tree. When unchecked (disabled), the layer has no effect on the shading of the scene. However, disabled layers are saved with the scene and are persistent across MODO sessions.
Invert: Inverts the illumination of the hair/fur producing a negative effect.
Blend Mode: Affects blending between different layers of the same effect type, allowing users the ability to stack several layers for different effects. For more on blending, please reference the 'Blend Modes' page of the documentation.
Opacity: Changes the transparency of the current layer. Reducing this value will increasingly reveal lower layers in the shader tree if present, or dim the effect of the layer itself on the surface.
INFO: Since the Hair Material uses a custom shading model to render the resulting Fur, it is not compatible with blending or masking techniques allowed by other layers. It should also be noted that even when using texture layers to drive individual Hair Shader channels, the Hair Material channel values will still affect the final result. This is because texturing only affects the single scattering of the hair material, but the multiple scattering calculations rely on the channels settings.


