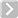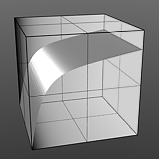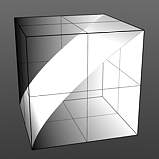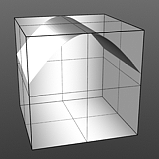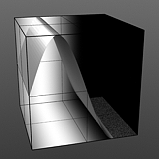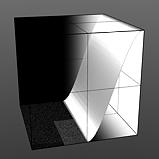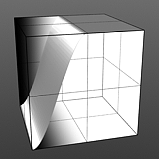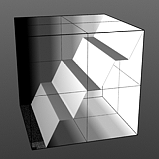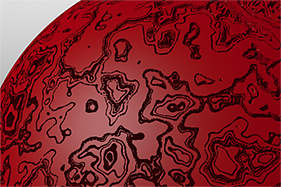

The Enhance:modo 'Waveform' layers are a special kind of Shader tree layer that produce no results by themselves, as they are meant to modify any like texture layer below them in the Shader Tree hierarchy. What this means is any texture layer, for example a 'Diffuse' layer would only be affected by a Waveform layer with its effect set to 'Diffuse' above it; in order to affect a 'Displacement' layer, the Waveforms layer effect will need to be changed to 'Displacement' as well. If there are multiple layers blended together of the same type, the waveform will only affect the nearest visible layer below it. Each Waveform type produces its own independent result.
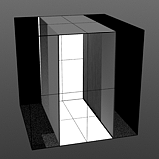
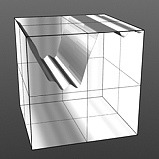
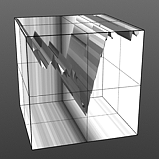
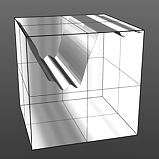
If you are familiar with the 'Curves' functionality of Photoshop, then it will be much easier to understand the 'Waveform' function, as it is a means to easily manipulate the values of the texture layer, just like curves affect the values in an image. If you were to make a graph of the input values of a surface versus the output values, the direct correlation between the two would be a straight line. As adjustments are made to the graph, the values mapped on the graph are adjusted. These adjusted values can adjust the shades of gray across a procedural texture or the shape of a displacement map. Consider this visual example below of a displaced plane on the far left. A gradient ramp has been applied to a flat plane and offset the same height as its width producing a ramp at a 45 degree angle. When a Waveform layer is applied to the gradient, it clearly demonstrates how the Waveform layer affect the values across the gradient ramp, illustrating the shaping ability that the Waveform function applies.
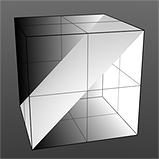 Displaced Plane |
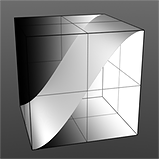 S-Curve Waveform |
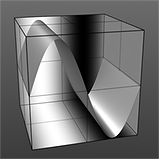 Sine Waveform |
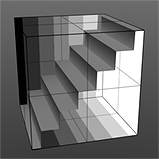 Stairs Waveform |
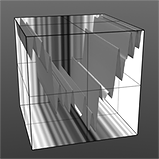 Noise Waveform |
To work with a Waveform layer, simply select the Material Group item in the Shader Tree that you wish place the texture into, and use the 'Add Layer' option, choosing one of the available Waveform options from the popup menu - "Add Layer > Enhance:modo Textures > Waveforms". For additional information regarding adding and working with Shader Tree Items Layers please reference the the Shader Tree page of the documentation. Each Waveform option produces its own unique results (with its name suggesting the shaping result of the layer). Users can further modify the attributes of the layer in the associated Properties panel adjusting from the various settings covered below.
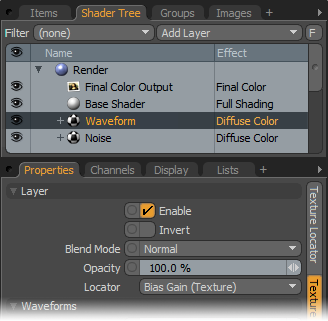 Layer--
Layer--
Enable: Toggles the effect of the layer on and off, duplicating the functionality of toggling visibility in the Shader Tree. When unchecked (disabled), the layer has no effect on the shading of the scene. However, disabled layers are saved with the scene and are persistent across modo sessions.
Invert: Inverts the RGB values for the layer producing a negative effect.
Blend Mode: Affects blending between different layers of the same effect type, allowing user the ability to stack several layers for different effects. For more on blending, please reference the 'Blend Modes' page of the documentation.
Opacity: Changes the transparency of the current layer. Reducing this value will increasingly reveal lower layers in the Shader tree if present, or dim the effect of the layer itself on the surface.
Locator: Most texture layers also have an associated 'Texture Locator' that is automatically created in the 'Item List'. This defines the mapping of the texture (the way it is applied) to the surface. The 'Locator' option sets that association. While users can choose alternate locators, the need to do so will be very rare; still, there are some possible instances where users may want multiple texture items to share a single locator. Since the Waveform layers affect the lower layers gray shades, the settings of the Locator, in this case, are unnecessary.
Waveforms--
The following section covers options specific to each type of Waveform.
Waveforms - Bias Gain --
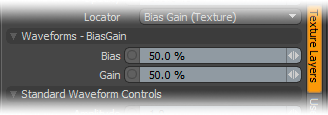
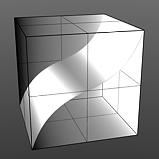
Bias: The Bias setting affects the attenuation (gradations) between the primary and secondary colors in a colored texture, or the gray values in a gray scale texture. Increasing this value will cause the texture to favor the primary color or value over the secondary whereas decreasing the value causes the secondary color or value to be favored.
 Bias 0% |
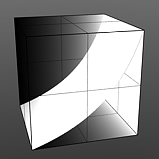 Bias 25% |
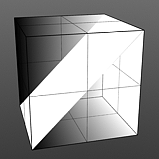 Bias 50% |
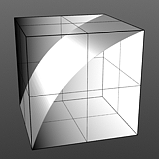 Bias 75% |
 Bias 100% |
Gain: The Gain setting is similar to a contrast control that effects the falloff of the gradient ramp between the primary Color/Value and secondary Color/Value. Setting the Gain to 100% will create a very sharp contrast whereas setting the value to 0% would reduce the contrast between the two to almost imperceptible amount.
 Gain 0% |
 Gain 25% |
 Gain 50% |
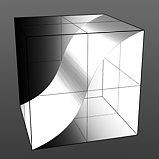 Gain 75% |
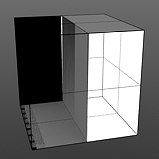 Gain 100% |
Waveforms - Fresnel --
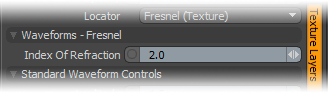
Index of Refraction: The Fresnel (pronounced Fruh-nell) effect is a phenomenon that describe particular refractive and reflective properties of a surface when the viewers angle relative to the surface changes. That particular rate at which the change happens is expressed in the Fresnel function and when applied to a gradient, such as one applied to the incidence angle of a surface, will produce the appropriate falloff rate. The Index of Refraction option will attenuate the Fresnel falloff rate based on the users input.
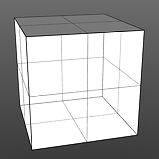 IOR 1.0 |
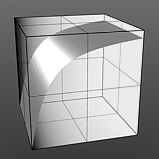 IOR 2.0 |
|
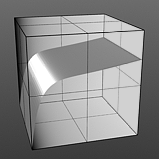 IOR 4.0 |
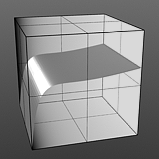 IOR 5.0 |
Waveforms - Gamma --
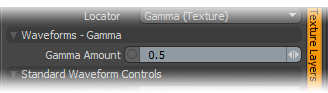
Gamma Amount: Gamma is a nonlinear adjustment function for manipulating the values across a spectrum. Like the Fresnel 'Index of Refraction' option above, the particular curve is expressed as a mathematical function. When applied to a texture layer, adjustments to the mid-tone value (those between black and white favoring the darker side) will match any gamma adjustment values applied to image map layers directly. A value of 1 will produce no results, as the output will match that of the input. Values lower than 1 will darken the gradient, while values larger than 1 will lighten it.
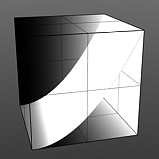 Gamma 0.5 |
 Gamma 1.0 |
|
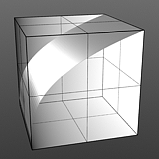 Gamma 2.0 |
 Gamma 3.0 |
Waveforms - Gaussian --
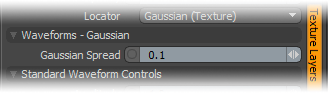
Gaussian Spread: A Gaussian distribution is a specific mathematical function that determines the spread of a number of values across a spectrum. When applied to a graduated texture layer, it will adjust the values based on this formula.
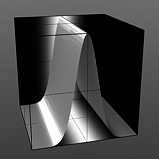 Spread 0.1 |
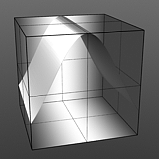 Spread 0.3 |
|
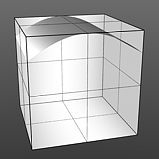 Spread 0.75 |
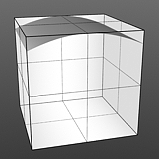 Spread 1.0 |
Waveforms - Impulse --
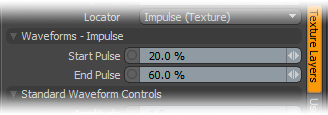
Start/End Pulse: The Impulse function will clamp the values of the gradient at the user defined 'Start' and 'End' positions and maximize all values in between.
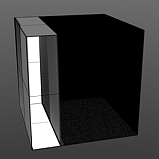 Start 0/End 25 |
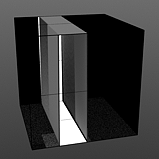 Start 25/End 50 |
|
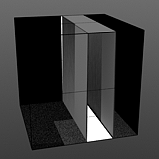 Start 50/End 75 |
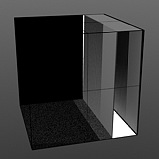 Start 75/End 100 |
Waveforms - Noise --
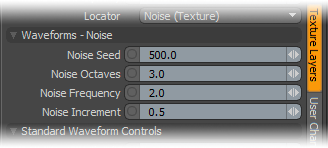
Noise Seed: The 'Seed' value is an initial value used when determining the noise that helps to randomize the generated. Different Seed values will produce dramatically or subtly different results.
Noise Octaves: The 'Noise Octaves' option determines the number of layers of noise that are combined to produce the final result. Greater numbers of Octaves will produce more randomized (detailed) results.
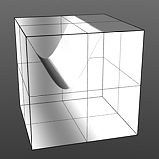 Octaves 1 |
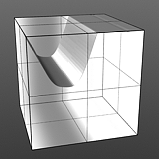 Octaves 2 |
|
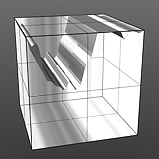 Octaves 4 |
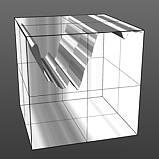 Octaves 5 |
Noise Frequency: The Frequency option determines the number of occurrences of the noise function when applied to the surface.
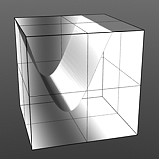 Frequency 1 |
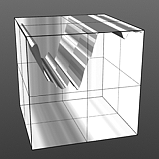 Frequency 2 |
|
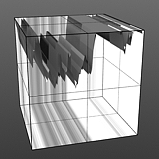 Frequency 4 |
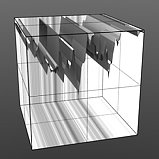 Frequency 5 |
Noise Increment: The Increment option, similar to frequency determines the number of noise bands across each frequency occurrence.
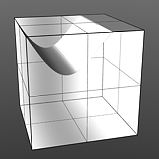 Increment 0.0 |
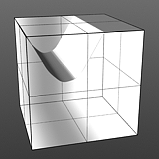 Increment 0.25 |
|
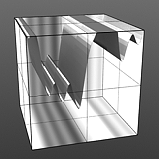 Increment 0.75 |
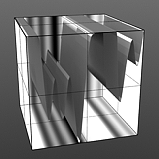 Increment 1.0 |
Waveforms - Ramp --
(Ramp has no user controlled settings)
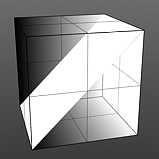
Waveforms - Rounded --
(Rounded has no user controlled settings)
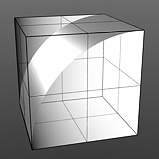
Waveforms - S-Curve --
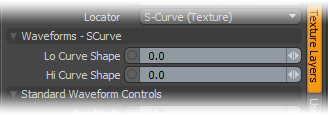
Lo Curve Shape: The S-Curve waveform function produces a smoothed curve across the graduated spectrum. The 'Lo Curve Shape' setting determines the low cutoff area for the gradient.
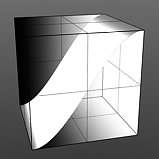 Low Curve 0 |
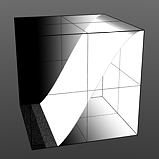 Low Curve 1 |
|
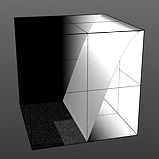 Low Curve 3 |
 Low Curve 4 |
Hi Curve Shape: The S-Curve waveform function produces a smoothed curve across the graduated spectrum. The 'Hi Curve Shape' setting determines the high cutoff area for the gradient.
 Hi Curve 0 |
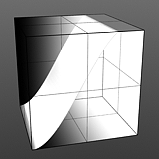 Low Curve 1 |
|
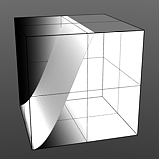 Low Curve 3 |
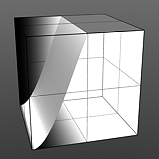 Low Curve 4 |
Waveforms - Sawtooth --
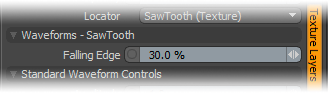
Falling Edge: The Sawtooth function produces a sudden minimum value drop in the graduated spectrum, with the position of the drop determined by the 'Falling Edge' option.
 Falling Edge 0 |
 Falling Edge 25 |
|
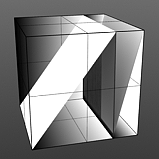 Falling Edge 75 |
 Falling Edge 100 |
Waveforms - Scallop --
(Scallop has no user controlled settings)
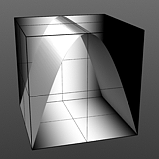
Waveforms - Sine --
(Sine has no user controlled settings)
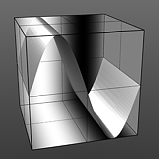
Waveforms - Smooth --
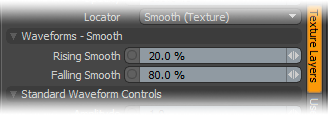
Rising/Falling Smooth: The Smooth function produces a result similar to what the Impulse function provides, by maximizing values between a low and high end, but between the minimum value to the Rise and the Fall to the maximum produces a smooth s shaped curve.
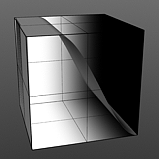 Rise 0/Fall 25 |
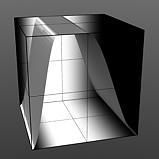 Rise 25/Fall 50 |
|
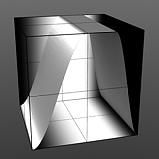 Rise 50/Fall 75 |
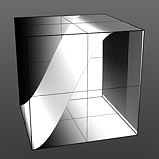 Rise 75/Fall 100 |
Waveforms - Smooth Impulse--
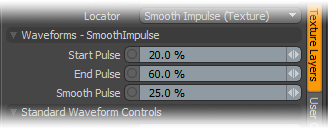
Start/End Pulse: The Smooth Impulse function is a cross between the Impulse function and the smooth function but allows the user to control the amount of smoothing of the result using the 'Smooth Pulse' option.
 Start 0/End 25 |
 Start 25/End 50 |
|
 Start 50/End 75 |
 Start 75/End 100 |
Smooth Pulse: Determines the amount of smoothing applied to the Impulse function.
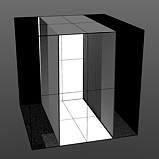 Smooth 0% |
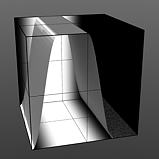 Smooth 25% |
|
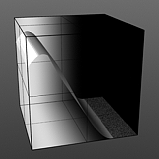 Smooth 75% |
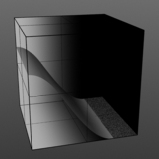 Smooth 100% |
Waveforms - Smooth Step--
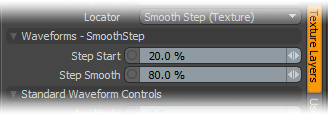
Step Start: Determines the start position for the smoothed step ramp.
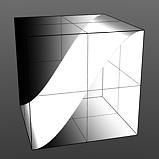 Start 0% |
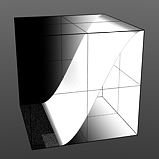 Start 25% |
|
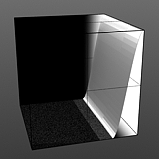 Start 75% |
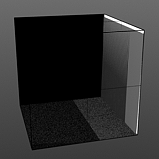 Start 100% |
Step Smooth: Determines the amount of smoothing applied to the step position.
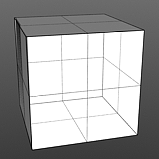 Smooth 0% |
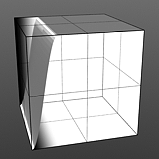 Smooth 25% |
|
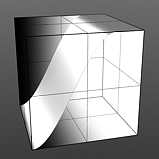 Smooth 75% |
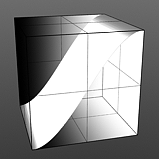 Smooth 100% |
Waveforms - Staircase --
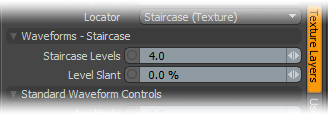
Staircase Levels: The Staircase function breaks the smooth gradations into specific discreet levels, producing a posterized effect. The number of discreet levels is determined by this option.
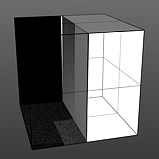 Levels 1 |
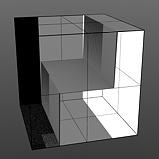 Levels 2 |
|
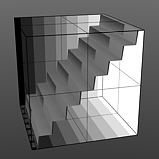 Levels 8 |
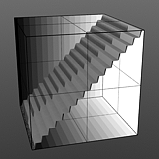 Levels 16 |
Level Slant: The 'Level Slant' option provides a way to interpolate between the step levels producing a less abrupt change from one step level to the next.
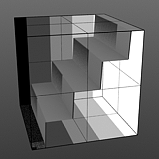 Slant 0% |
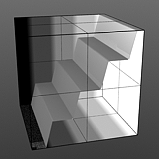 Slant 25% |
|
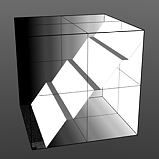 Slant 75% |
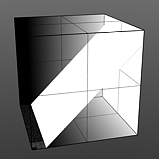 Slant 100% |
Standard Waveform Controls--
Amplitude: This value controls the maximum value of the Waveform scaling all other values in relation to the maximum.
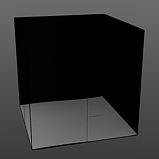 Amplitude 0% |
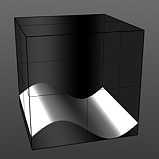 Amplitude 25% |
|
 Amplitude 75% |
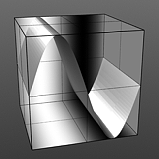 Amplitude 100% |
Frequency: This value controls the number of waveform occurrences in a single cycle. Waveform will only cycle multiple times when the 'Repeat' option is enabled.
 Frequency 1 |
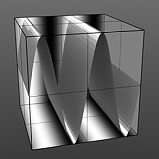 Frequency 2 |
|
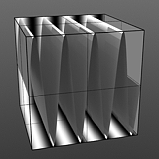 Frequency 4 |
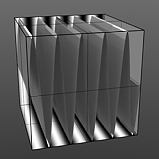 Frequency 5 |
Phase: This value moves the waveform forwards and backwards.
 Phase 0% |
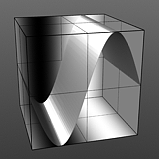 Phase 25% |
|
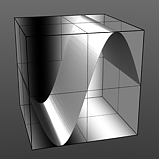 Phase 75% |
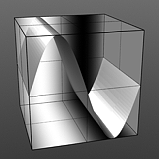 Phase 100% |
Shift: This value moves the waveform up and down.
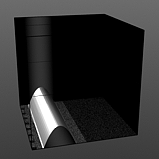 Shift 10% |
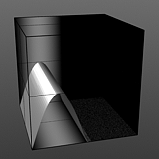 Shift 25% |
|
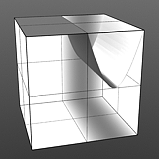 Shift 75% |
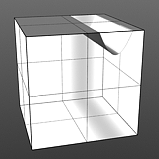 Shift 90% |
Lower Clip: This value determines a clip level for the Background Color/Value, truncating values beyond the defined setting and scaling those that remain. Combined with the Upper Clip value, users can apply this option to extend or contract the total range of values for the texture.
 Low Clip 0% |
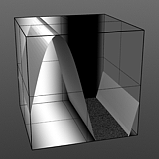 Low Clip 25% |
|
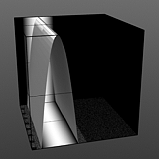 Low Clip 75% |
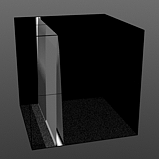 Low Clip 100% |
Upper Clip: This value determines a clip level for the Foreground Color/Value, truncating values beyond the defined setting and scaling those that remain. Combined with the Lower Clip value, users can apply this option to extend or contract the total range of values for the texture.
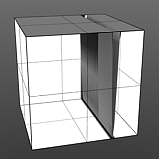 Upper Clip 0% |
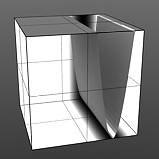 Upper Clip 25% |
|
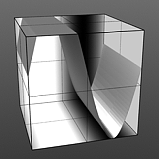 Upper Clip 75% |
 Upper Clip 100% |
Invert: This option flips the waveform vertically.
Repeat: This option repeats the waveform, useful when the frequency option is set beyond a value of 1.
Reverse: This option flips the waveform horizontally.
Triangle: This options allows the waveform to be mirrored on it's own axis.
Output Controls--
Background Color/Value: This value determines the Color (or Value) of the texture's Background area, which will ramp toward the Foreground Color/Value.
Background Alpha: This value determines the Alpha transparency of the Background Color.
Background - Use Last Layer: When this option is enabled the Background Color area will be completely transparent, revealing the shading results of any lower layers.
Foreground Color/Value: This value determines the Color (or Value) of the texture's Foreground area, which will ramp toward the Background Color/Value.
Foreground Alpha: This value determines the Alpha transparency of the Foreground Color.
Foreground - Use Last Layer: When this option is enabled the Foreground Color area will be completely transparent, revealing the shading results of any lower layers.
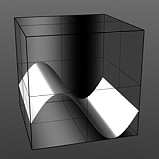
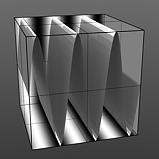
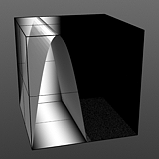
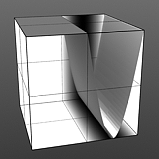
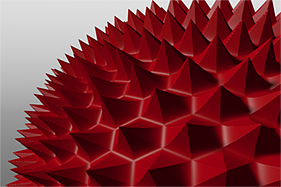
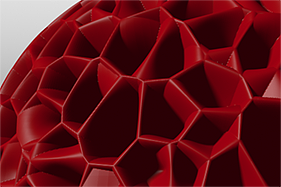
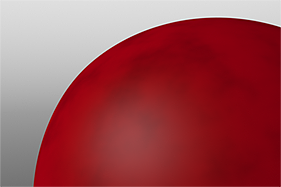
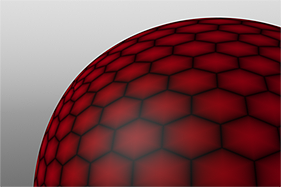
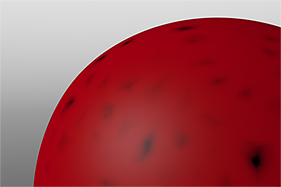
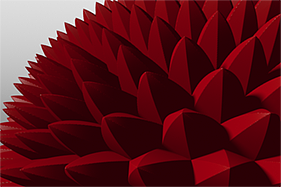
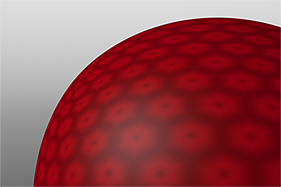
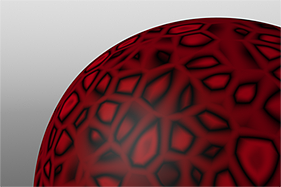
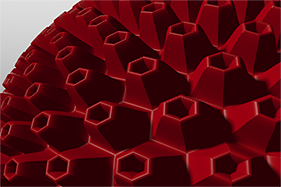
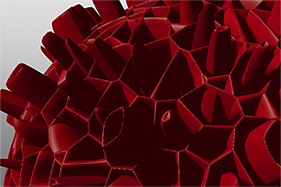
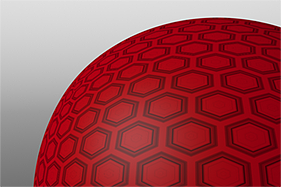
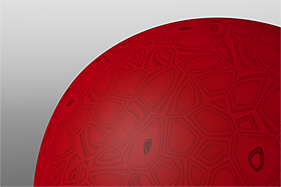
Waveforms in Use
Here is a collection of rendered images using the Waveform functionality.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|